| Command | Description |
|---|---|
git remote |
Manages remote repositories |
git clone |
Creates a local copy of a repository |
git pull |
Fetches and merges the latest changes from a remote repository into the current branch |
git fetch |
Updates remote tracking branches |
git push |
Uploads local commits to a remote repository |
Session 7: Collaboration on GitHub / GitLab
Track, organize and share your work: An introduction to Git for research
Course at Zentralinstitut für Seelische Gesundheit
Wednesday, 29th of January 2025, 15:00
1 Last session: Integration with GitHub / GitLab
Last session: Learning objectives
After the last session, you should now be able to answer the following questions / do the following:
💡 You can create a remote repository.
💡 You can connect your local Git repository to a remote repository service like GitHub or GitLab.
💡 You can pull and push changes to and from a remote repository.
💡 You can clone a repository from a remote repository.
Last session: Cheatsheet
Last session: recipes project
At the end of this session, you should have accomplished the following:
- You created a GitHub account.
- You connected your GitHub account to your local Git using SSH.
- You created a new private(!) GitHub repository.
- You uploaded (i.e., “pushed”) the default branch of your
recipesrepository to GitHub.
Collaboration Option 1:
- You invited a partner from the course as a collaborator to your
recipeson GitHub. - You collaborated on a shared project by adding and committing changes to your partner’s repository.
Collaboration Option 2:
- You clone your own repository to a different location on your computer.
- Stage and commit changes in the repository in this new location.
- Push the changes to GitHub and pull them in the original repository location on your computer.
Optional:
- You created a short
README.mdfile in your repository.
Please keep the recipes folder! We will continue to use it in the following sessions.
2 This session: Collaboration on GitHub / GitLab
This session: Collaboration on GitHub / GitLab
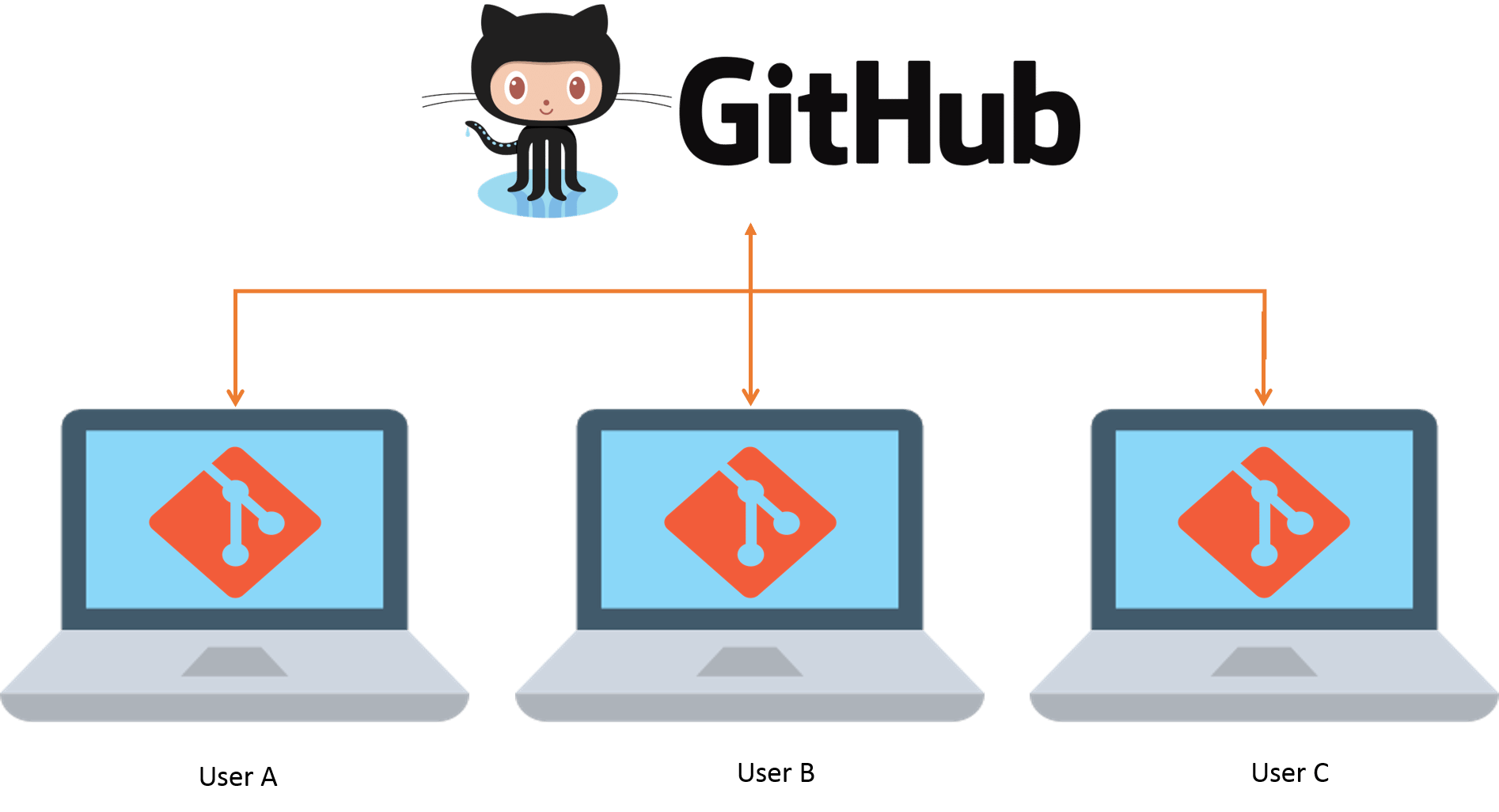
Image from Techdobz
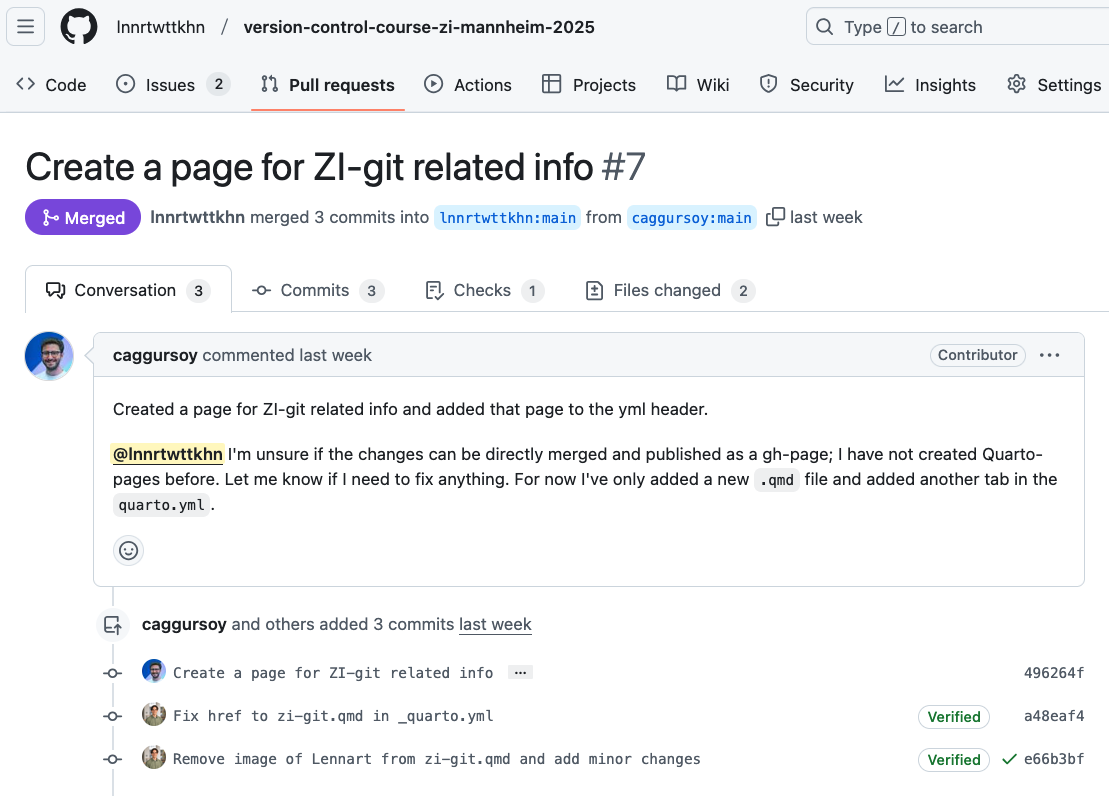
This session: Forking & Pull Requests
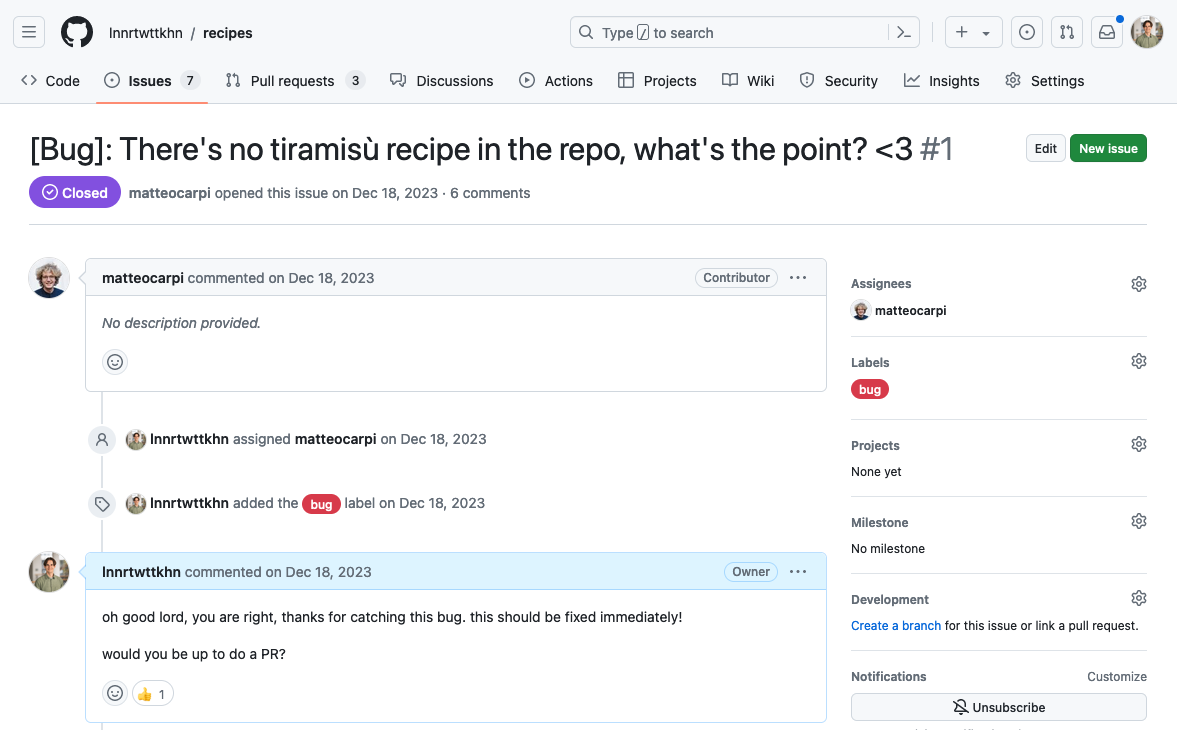
This session: Issues
Reading
Learning objectives
Remotes - Advanced
💡 You know the purpose and components of a Pull Request.
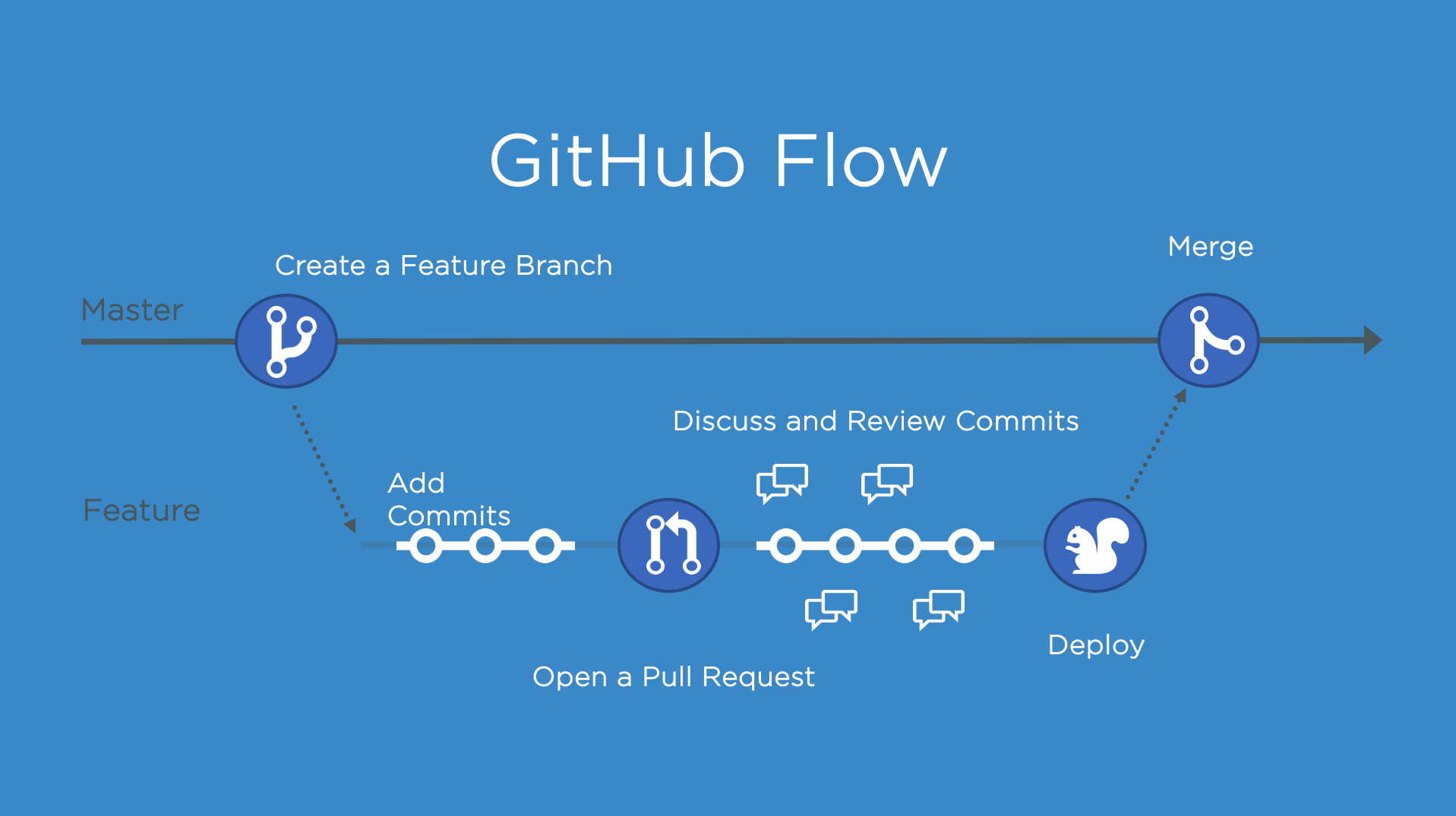
💡 You know how to collaborate using the popular workflow strategy GitHub flow.
💡 You know the purpose and components of a README file.
💡 You can fork a repository.
💡 You can create a Pull Request from a forked repository.
💡 You can protect your main branch.
Issues
💡 You understand the purpose of GitHub Issues.
💡 You can create and manage Issues.
💡 You can reference an Issue in another issue.
💡 You can close an Issue with a commit or pull request.
Cheatsheet
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
git remote |
Manages remote repositories |
git clone |
Creates a local copy of a repository |
git pull |
Fetches and merges the latest changes from a remote repository into the current branch |
git fetch |
Updates remote tracking branches |
git push |
Uploads local commits to a remote repository |
GitHub Flow
Tasks
In this session, you will work on the following tasks:
- Reading: Read the chapter(s) “GitHub - Advanced” and “Issues” in the Version Control Book.
- Implementation: Try out the commands in the chapter.
- Exercises: Work on the exercises for the
recipesproject. - Quiz: Test your knowledge with the quiz.
As always:
- Try out the commands of this session and play around with them.
- Check whether you have achieved the learning objectives.
- Ask questions!
- Let’s git started!
recipes project
At the end of this session, you should have accomplished the following:
- You forked a public / internal
recipesrepository of another course participant. - You opened an Issue in another repository.
- You created a pull request with changes that “fix” the Issue you opened.
Please keep the recipes folder! We will continue to use it in the following sessions.
Exercises
“Public” collaboration with pull requests (using a fork and GitHub Flow)
- Find out what forking is.
- Fork the project repository of the course instructor or another course participant (ideally, someone who is not your collaborator from the previous exercise).
- Create an Issue in your new collaborator’s repository, indicating an entry that you think is still missing in their repository.
- Repeat the steps from the exercise on collaboration with remote repositories using the forked repository:
- Clone the forked repository to a sensible location on your computer.
- Create a new branch and make one or multiple commits “fixing” the Issue that you opened. If available, follow the contributing guide of your collaborator’s repository.
- Push your changes to the remote repository.
- Create a pull/merge request with your changes (hint: from the forked to the original repository) and refer to the Issue in your pull/merge request.
Use Lennart’s recipes repository. Find out about the contributing guidelines in Lennart’s repo and follow them when creating a new recipe.
Reviewing pull requests
- View any pull requests that are created in your
recipesrepository. - Review the changes made by the contributor in the pull request.
- If needed, discuss additional changes with the contributor in the pull request.
- Close the pull request by merging the proposed changes.
Solutions
- Forking is a process where you create a copy of someone else’s repository under your own account. It allows you to freely experiment with changes without affecting the original project.
- To fork the project repository of another course participant: (1) Go to the GitHub repository you want to fork. (2) Click the
Forkbutton at the top-right corner of the repository page. (3) Select your GitHub account to fork the repository. - Create an Issue, suggesting a missing entry: (1) Go to the Issues tab of your partner’s repository on GitHub. (2) Click
New issue. Provide a title and description for the Issue, suggesting a missing entry. (3) ClickSubmit new issue. - Clone the forked repository to a sensible location on your computer.
- Create a new branch and create one or multiple commits “fixing” the Issue that you opened.
- Push your changes to the remote repository:
Create a pull request with your changes (from the forked to the original repo) and refer to the issue in your pull request:
- Go to your forked repository in your browser.
- Click the
Compare & pull requestbutton. - Ensure that the base repository is the original and the base branch is
main. - Provide a title and description for your pull request.
- Refer to the issue by adding
Fixes #issue-numberin the description. - Click
Create pull request. - Review any pull requests in your repository.
Version Control Course
